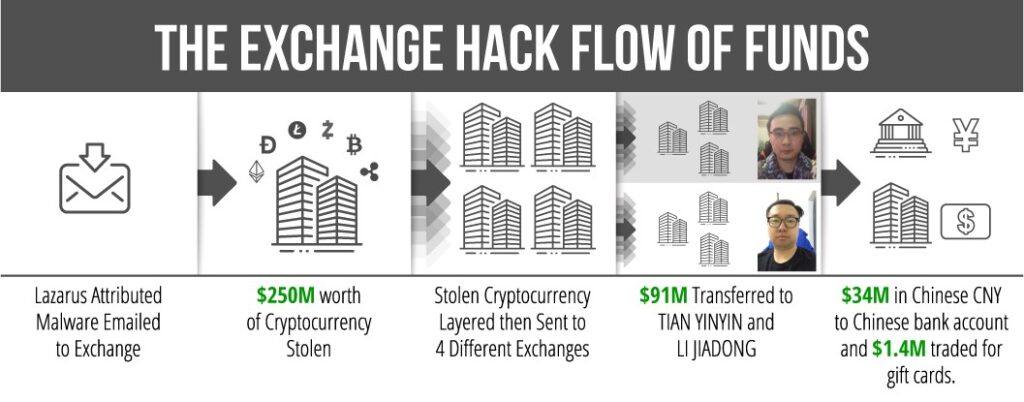
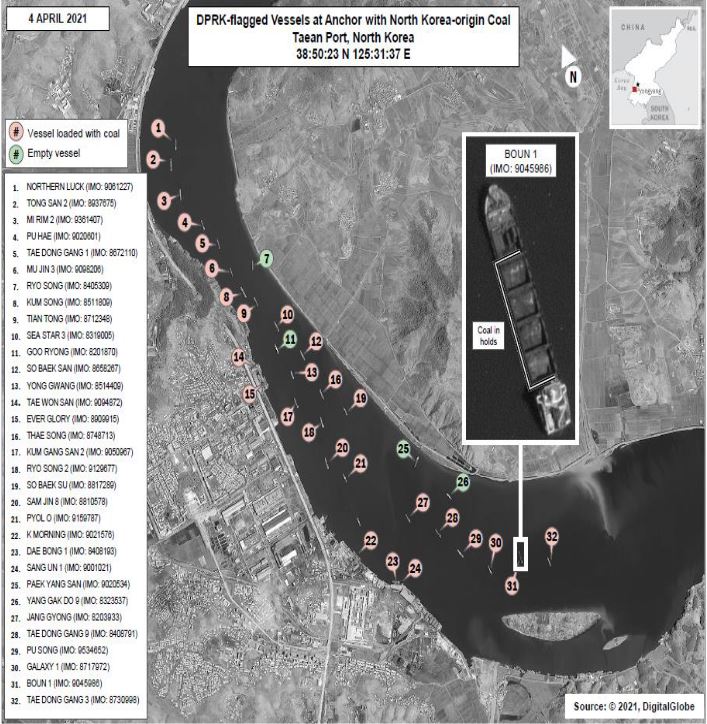
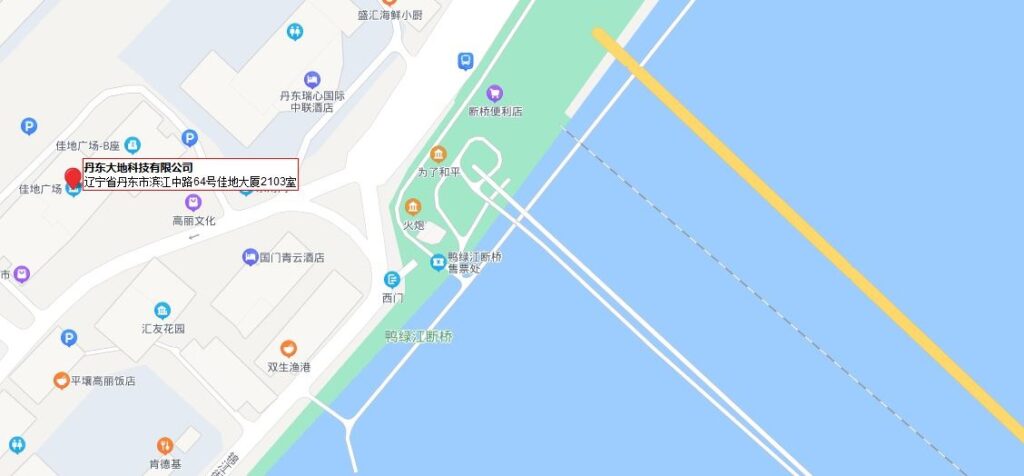
June 24, 2022 was a day of significance as it marks the 48th anniversary of diplomatic ties between the DPRK and The Lao People’s Democratic Republic. The friendship and cooperation between the two countries was forged and deepened through historic summits of 1965 and 1970 between Kim Il Sung and leader of Lao people- Kaysone Phomvihane. Today, the DPRK government remain unchanged in their resolve to develop the relations of ‘friendship’ with Laos.
Pyongyang Papers asks the question, “does DPRK need Laos more than Laos needs DPRK?” We would suggest that the DPRK only need Laos as a money generator for the regime and therefore have no problem severing any ties if they do not get what they want i.e. money. So, is this true friendship?
North Korean restaurants in Laos
With easing of COVID-19 travel restrictions in Asia, people have been able to travel again. The backpacker trail is opening up with travelers seeking out new experiences.
Pyongyang Papers has been tipped off by a backpacker that restaurants in Laos are still operating using North Korean workers. Despite UN Security Council resolution 2397 requiring all Member States to repatriate, by December 22, 2019.
All North Korean entities (including restaurants) are supposed to have been closed down under UN sanctions which prevent North Korea from having overseas workers. It is well documented that North Korea exploit their citizens by sending them abroad to earn foreign currency which is then sent back to the hermit state. These restaurants are another example of this, and the money is certainly not for the good of the impoverished, starving people but more likely end up funding weapons of mass destruction.
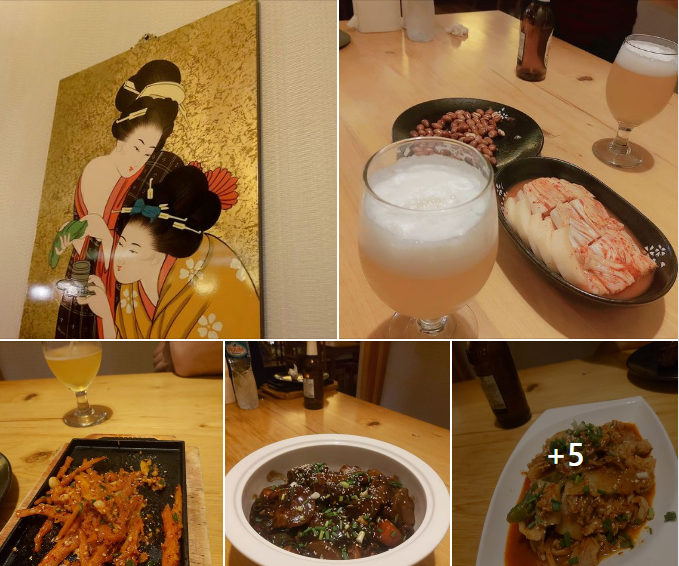
Our backpacker found a very unusual dining option in Vientiane, 원언니식당 (Won Onni Sikdang) – which translates to Big Sister Won’s restaurant. This restaurant, conveniently located close to the DPRK Embassy in Vientiane, doesn’t offer Laos cuisine, but instead seems to be a North Korean restaurant and has multiple 5-star reviews on Google.
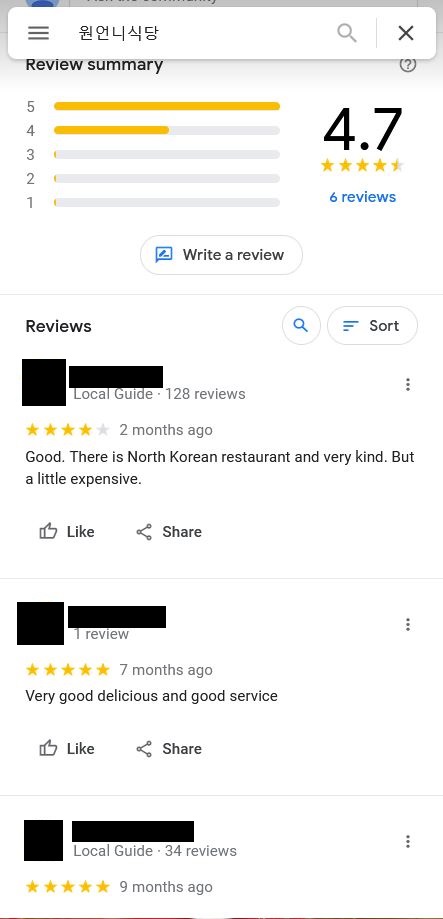
So what’s in it for the DPRK regime? Sources confirm that the North Korean restaurant menu requests payment in US dollars and not Laotian Kip. This is another way that the DPRK can seek to launder its ill-gotten gains, and a source of foreign currency for the regime. We don’t believe that this is just a business set up by an enterprising North Korean expatriate. Any North Korean restaurant will certainly have to pay a retainer or fee to the DPRK embassy in Laos just in order to operate, which is forwarded onto the DPRK regime.
According to the 2022 UN Panel of Experts report, Big Sister Won’s restaurant is not the only North Korean restaurant believed to still be in operation in Laos. The UN report details four North Korean restaurants and one night market, including their locations and images, which appear to have continued to operate “even after the applicable measures towards the closure of the restaurants and repatriation were taken by the Laotian authorities in 2020”. This is a direct violation of the December 2019 United Nations Security Council Resolution (UNSCR) 2397.
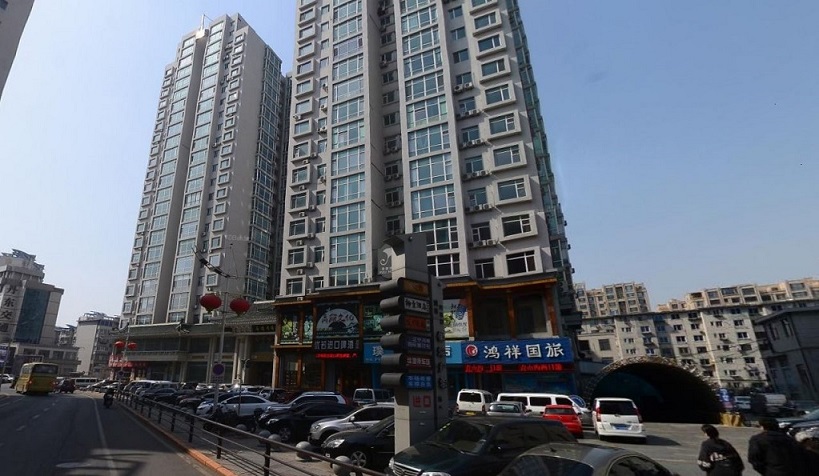
Kumkangsan Restaurant
The UN report however does not mention Big Sister Won’s restaurant, it seems this one may have slipped under the radar somehow. Our sources have informed us of another North Korean restaurant in Vientiane; Kumkangsan Restaurant (ອາຫານ ຄຶ່ມກ່າງຊານ) on Asean Road, Sisavath Village, Vientiane. The Kumkangsan restaurant seems to have a shop attached- we wonder what they sell?

The latest UN Panel of Experts report states that Laotian authorities took action against the North Korean restaurants in 2020 but our investigation proves that more needs to be done to stop the regimes illicit activity in Laos. Pyongyang Papers is still investigating DPRK run restaurants in Laos and would like to hear from you if you have any further information on the entities named in this article or any other individuals and entities helping the North Korean regime avoid sanctions so that we can investigate further.